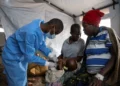
Western Europe is facing a growing crisis as diphtheria cases continue to rise, with new research revealing the worst surge in 70 years. This highly infectious disease, once thought to be a thing of the past, is now a major concern for public health authorities, especially as it is hitting the most vulnerable populations the hardest.
According to the latest data, the number of diphtheria cases in Western Europe has skyrocketed since 2022, with a significant increase in cases among migrants and the homeless. This is a worrying trend, as these populations often have limited access to healthcare and are at a higher risk of contracting the disease.
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection that mainly affects the respiratory system. It is highly contagious and can spread through coughing, sneezing, or even through contact with the skin or objects contaminated with the bacteria. The infection can cause severe inflammation of the throat and can lead to difficulty breathing, heart failure, and even death if left untreated.
The recent surge in diphtheria cases in Western Europe has been attributed to several factors, including the influx of migrants from countries where the disease is still prevalent, such as Syria and Afghanistan. The living conditions in refugee camps and homeless shelters also make it easier for the bacteria to spread.
The new research, which was revealed on Wednesday, sheds light on the severity of the situation and highlights the urgent need for action. It is a wake-up call for governments and healthcare authorities to take immediate steps to contain the spread of the disease and provide necessary aid to those affected.
One of the major challenges in tackling this diphtheria surge is the lack of awareness about the disease. Many people, especially in Western Europe, may be unfamiliar with diphtheria, as it has been effectively controlled through vaccination programs in the past. However, due to the recent surge, there is a pressing need for increased awareness campaigns to educate the public about the symptoms, prevention, and treatment of diphtheria.
It is also crucial for governments to ramp up their vaccination efforts, particularly among vulnerable populations. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent diphtheria, and it is essential to ensure that everyone has access to it. This includes providing free vaccinations to migrants and the homeless, who may not have the means to afford them.
In addition to vaccinations, it is essential to improve living conditions in refugee camps and homeless shelters to prevent the spread of the disease. Adequate sanitation and hygiene facilities, as well as access to clean water, are crucial in controlling the spread of diphtheria.
Moreover, there is a need for increased cooperation and coordination among European countries to tackle this crisis. Diphtheria knows no borders, and it is crucial for countries to work together to prevent its further spread. This includes sharing information, resources, and expertise to effectively combat the disease.
The good news is that diphtheria is a preventable and treatable disease. With proper vaccinations and prompt medical care, the mortality rate of diphtheria is relatively low. However, if the current surge is not addressed promptly, it could have devastating consequences.
In conclusion, the recent surge of diphtheria in Western Europe is a cause for great concern. It is hitting the most vulnerable populations the hardest and requires immediate action from governments and healthcare authorities. Increased awareness, vaccination efforts, and improved living conditions are crucial in containing the spread of the disease. Let us all work together to prevent the further spread of diphtheria and protect the health of our communities.





![Complete BritRail Pass Guide [Types, How to Use It, Pros + Cons]](https://inside-news.uk/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/00221EB4-BCA2-4DBB-6CD4-83DBC37D71FA-120x86.webp)